Culture of learning – a culture that appreciates and promotes opportunities to grow at work – is an excellent way to improve well-being. Learning and career advancement opportunities improve job satisfaction, productivity, and the long-term viability of an organization. Continuous training is an investment into your organization’s human capital.
Simply adopting a new training program or offering a range of online trainings is not a silver bullet, however. Staff engagement is a prerequisite of a successful training program – so implementing new training opportunities may also require a shift in organization culture.
Managing a culture of learning can be challenging. Often the main problem is the time horizon – it may be difficult to justify long-term reforms in a context where short-term savings are prioritized.
So what can HR do to make upskilling more attractive for employees?
The building blocks of a culture of learning
Managing a culture of learning is an interesting field that has been extensively researched. There is a broad selection of different theoretical models on understanding culture. In this article we use a three-tiered model that emphasizes the tools of upskilling. It is practice-oriented and helps manage HR’s work.
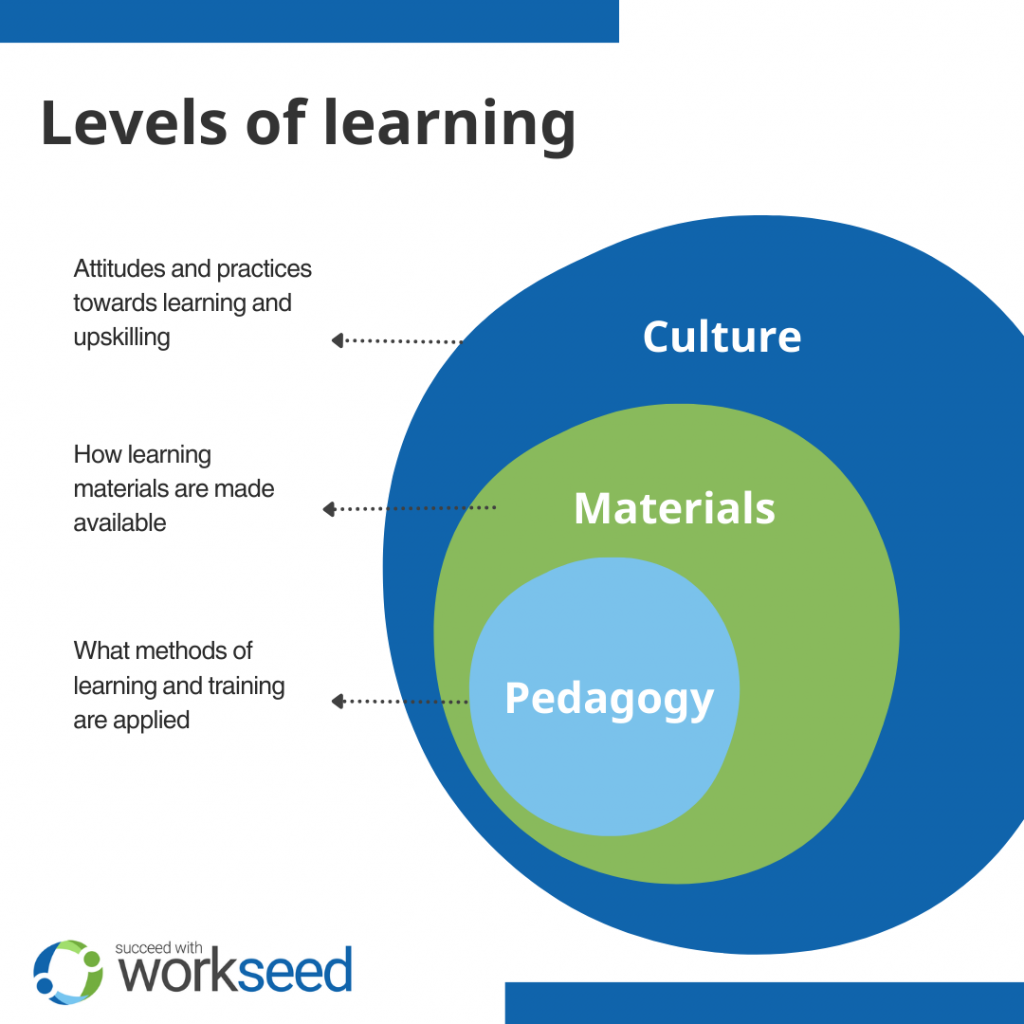
The model divides culture into hierarchical levels from organizational values to practice.
The first level is the organization’s culture, values, and practices. They define how learning is viewed and valued – why training takes place, what kind of goals training aims to achieve, and what metrics can be used to measure training success.
The second level is that of learning contents and courses. This level defines how resources are allocated, what kind of skills are prioritized, how training programs and actual work are related, and how employees can influence training programs within the organization. On this level concrete learning and organizational strategy meet.
The third level is that of pedagogy and tools. This is the most concrete level that defines how learning tools and environments are implemented, how learning takes place, and what learning looks like. This level defines how day-to-day workflows are created and how they can be improved.
Level of culture: Nurture appreciation for learning
Understand your goals. An organization needs to understand what it wants to achieve with training and upskilling. Business goals define how a relevant training program should be built. Fostering a culture of learning is like any management project: understanding goals is half the effort.
Do you want to assure there is a streamlined and cost-effective on-boarding program for new employees? Organizations with large staff and high turnover might benefit from a clear process for new employees to save money and guarantee steady quality and legal compliance.
Or do you want to provide opportunities for continued training and professional growth in the long term? Training can help to reduce skill gaps and guarantee that there is no shortage of people with relevant key skills.
Offer the right incentives. Whatever the priorities of the organization, training opportunities should be appreciated. Employees should have an incentive to participate. That is, upskilling and career progression should go hand in hand. When participating in training translates into new career opportunities, upskilling policy has real impact.
Develop training initiatives transparently. Do not develop training programs in isolation. Let the entire organization participate in developing new training programs and courses. Collect feedback, accept suggestions, and keep your mind open. Create an environment where it is safe to provide feedback. Follow up on your training initiatives and develop them iteratively.
An organization’s culture constitutes the basis of how training opportunities are received. Even the best training programs will fail to benefit the organization if people do not participate in training.
Level of training materials – Offer relevant contents
A training program and materials should be designed to be practical and relevant for employees. How are contents created, what should they cover, how are they provided to employees, and how can employees provide inputs for further developing the materials?
Opportunities to participate. The most crucial single factor is the ability to participate in training courses. There is little point in providing learning opportunities if there is no sufficient free time after normal working hours. Opportunities to participate should also be clearly communicated – who is going to attend, if they do not even know the training is taking place?
Provide training clearly. It is important to consciously design the infrastructure used to offer training. Do the employees find the materials they need, are there enough resources, is it easy to find the most interesting contents? Is it possible to take courses flexibly enough?
Adapt to individual needs. Learning can be a very versatile process. Different learners learn at different pace and are interested in different things depending on their background, personality, and preferences. The more the training modules adapt to individual needs, the better.
Create relevant contents. The course catalog should be useful and interesting to the users. Collecting continuous feedback and involving employees in designing training programs is central to pedagogic design. Freedom to choose which training modules to take also increases study motivation.
At best the training materials work both on the long and the short term. Optimally participating in trainings helps employees to succeed in their current job – but also opens new career opportunities in the future.
Level of learning – Provide the right tools
At the most practical level it is important to understand how day-to-day learning takes place. Is learning meaningful and efficient, is the pedagogical method impactful, and are the best possible tools applied? If the platform is subpar, even a good training program will likely be under-used. A culture of learning is difficult to manage without tools on the grassroots level.
Make learning flexible. It is usually difficult to justify full days of face-to-face training sessions. It is often difficult to coordinate good occasions, and employees usually cannot interrupt work at will. The opportunity to study independently of place and time is usually the best alternative. In many organizations it is also important to make training materials available also on mobile devices.
Divide studies in modules. Dividing study materials into small chunks makes them more accessible. Offer micro courses or divide longer courses into smaller sections. Smaller modules make pacing studies easier, and allows for adapting training into individual needs.
Create a resource repository. It is useful to make study materials available for later use. Employees may not only benefit from taking courses, but also from having access to the course materials in their daily work. This way they can consult study materials and their notes during work, for instance on their work computer or mobile devices. This can be particularly useful for technical training and for training materials that are regularly updated.
Facilitate peer learning. Online courses are an excellent medium for social and peer learning. At minimum, it is easy to integrate elements such as discussion forums and peer reviews into online courses. At best, HR can facilitate sharing ideas and studying in groups.
How do I foster culture of learning in my company?
Creating a culture of learning or a successful training programs is a complex task. Maybe the most crucial element of such a program is a suitable tool that allows for easily creating contents, completing courses, and monitoring training impact.
Workseed is an LMS for working-life oriented learning. It is already in use in many companies in services, industry, retail, and administration.
Its most important features are flexible and easy on any devices, adapting studies to individual needs, extensive monitoring tools, and intuitive user interface. It can provide the tools and infrastructure needed to kick start a culture of learning in any organization.
For instance Jungle Juice Bar trains its new Juice Masters on Workseed flexibly. You can read the full customer story here.
In case you want to know more about Workseed features, you can book a demo here. Our experts can help you improve learning at your organization.










